iOS Development Notes
Basics
-
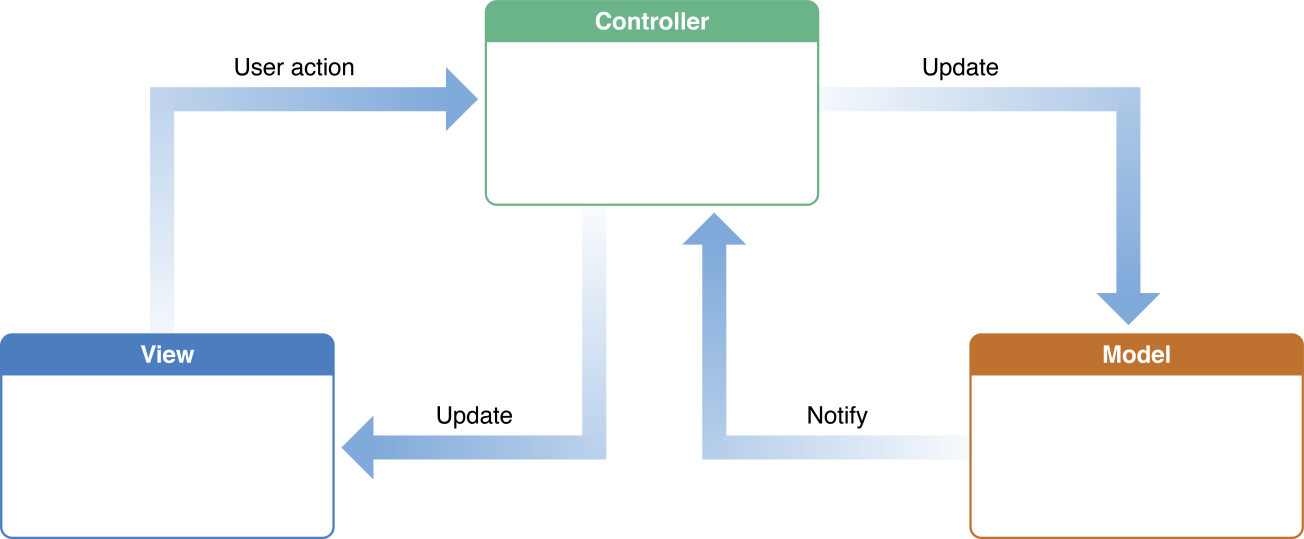
Model-View-Controller is a design pattern in iOS.
-
Unlike in Android Studio, the Interface Builder is not a graphical representation of code. A storyboard file is an archive of object instances.
-
Outlets are references to objects:
@IBOutlet var questionLabel: UILabel!(IB means interface builder.) (Right click the item and drag it to the assistant editor to create the outlet.) -
Actions:
@IBAction func showNextQuestion(_ sender: UIButton) {}(Right click the item and drag it to the assistant editor to create the action.) -
Use
View Controllerto add new screens. Use Embed in >Navigation Controllerto add a nav controller. -
Use this to pass info between screens:
1 2 3override func prepare(for segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: Any?) { segue.destination.navigationItem.title = textField.text } -
Use
performSegueto create a segue programmatically (could be used for conditional segue.)1performSegue(withIdentifier: "Foo", sender: nil) -
Right click and drag to a view controller to add the new view controller to the Tab Bar Controller (select view controllers).
-
Connect the new ViewController file by setting the custom class attribute in storyboard.
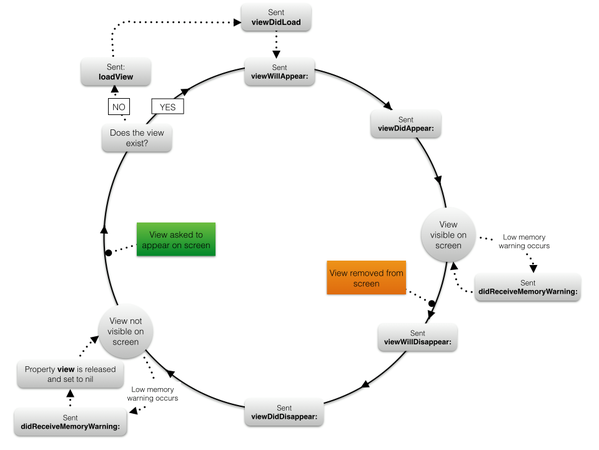
View Controller Lifecycle:
-

-
Detailed methods: https://guides.codepath.com/ios/View-Controller-Lifecycle
MVC Architecture
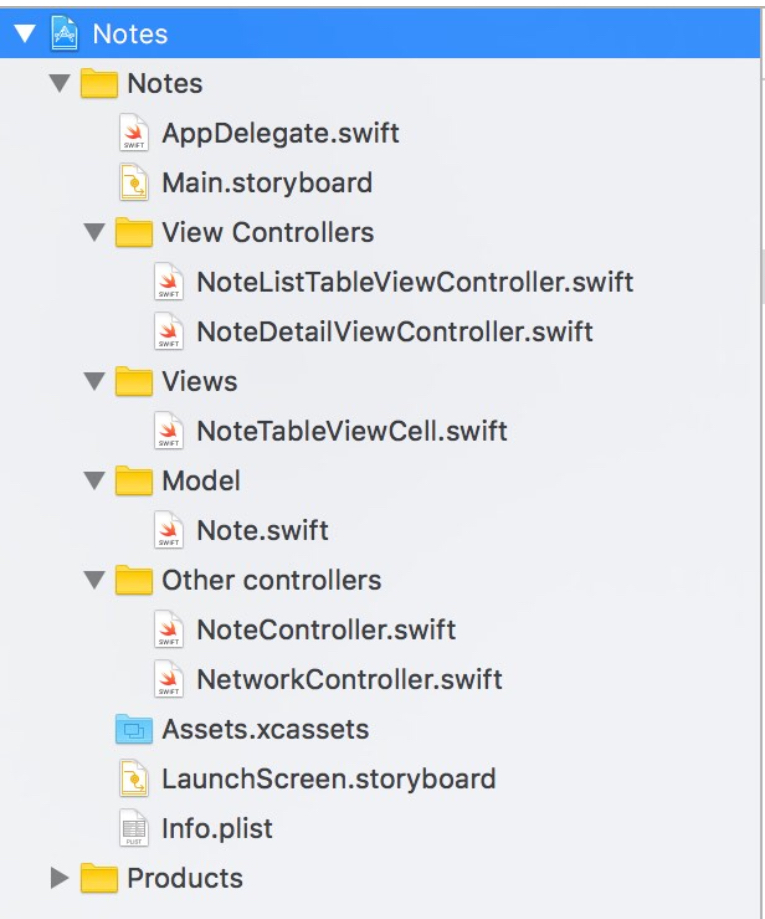
Project Organization
- Example:

References
-
App Development With Swift